
Luteolin As a Health Supplement
Abstract:
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid abundant in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs, has garnered significant attention due to its diverse pharmacological properties. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the pharmacological potential of luteolin, encompassing its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective activities. We discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying these pharmacological effects, highlighting luteolin's ability to modulate various signaling pathways and interact with molecular targets implicated in disease pathogenesis. Furthermore, we explore the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and safety profile of luteolin, along with its potential limitations and future directions for research and therapeutic applications.
Discover Luteolin
Keywords: luteolin, flavonoid, pharmacological properties, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, neuroprotection, cardioprotection
Introduction:
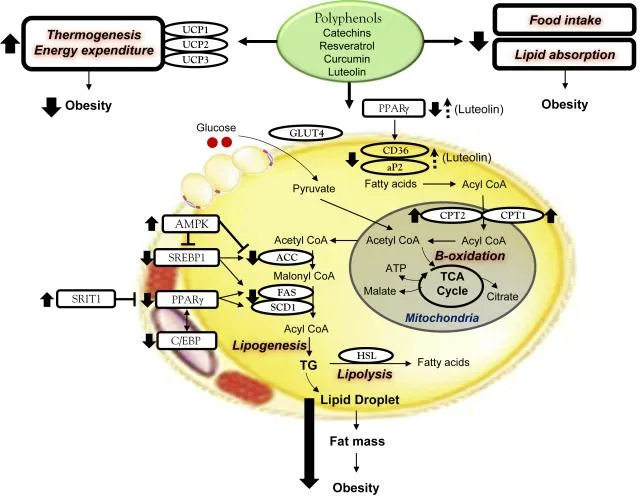
Flavonoids, a class of polyphenolic compounds ubiquitous in plants, have gained considerable attention in recent years owing to their diverse pharmacological properties and potential health benefits. Among these, luteolin (3′,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone), a flavone commonly found in fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has emerged as a promising candidate for various therapeutic applications. Luteolin exhibits a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective effects, making it a subject of intense scientific investigation.
Pharmacological Properties:
2.1 Antioxidant Activity:
Luteolin exerts potent antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These antioxidant properties contribute to its protective effects against oxidative stress-related diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
2.2 Anti-Inflammatory Activity:
Through modulation of inflammatory signaling pathways such as nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), luteolin exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects. It suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory mediators, thereby attenuating inflammation and alleviating symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
2.3 Anticancer Activity:
Luteolin demonstrates promising anticancer properties attributed to its ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation, induce apoptosis, and suppress tumor growth and metastasis. It exerts these effects through multiple mechanisms, including regulation of cell cycle progression, modulation of apoptosis-related proteins, inhibition of angiogenesis, and suppression of oncogenic signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt/β-catenin.
2.4 Neuroprotective Activity:
The neuroprotective effects of luteolin stem from its ability to mitigate oxidative stress, inhibit neuroinflammation, and modulate neuronal signaling pathways implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke. Luteolin enhances neuronal survival, promotes synaptic plasticity, and protects against neurotoxic insults, thus offering potential therapeutic benefits for neurological disorders.
2.5 Cardioprotective Activity:
Luteolin exerts cardioprotective effects by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and endothelial dysfunction, thereby mitigating risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and myocardial infarction. It improves vascular function, reduces lipid accumulation, and enhances myocardial contractility, highlighting its potential as a cardioprotective agent.
Molecular Mechanisms:
The pharmacological effects of luteolin are mediated through modulation of various molecular targets and signaling pathways involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and neuronal function. These include transcription factors (e.g., NF-κB, AP-1), kinases (e.g., PI3K, Akt, MAPK), apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bax, caspases), growth factors (e.g., VEGF, PDGF), and neurotransmitter receptors (e.g., NMDA, AMPA). By interacting with these targets, luteolin exerts pleiotropic effects that underlie its pharmacological actions in different disease contexts.
Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile:
Despite its potent pharmacological properties, luteolin exhibits limited bioavailability due to factors such as poor solubility, rapid metabolism, and extensive first-pass metabolism. Strategies to enhance its bioavailability, such as formulation with bioenhancers or nanocarriers, are being explored to improve its therapeutic efficacy. Luteolin is generally considered safe at dietary levels, with low toxicity and minimal adverse effects reported in preclinical and clinical studies. However, further research is needed to elucidate its long-term safety profile and potential drug interactions.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives:
Luteolin holds immense promise as a multifaceted pharmacological agent with diverse therapeutic applications across various disease conditions. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective properties make it an attractive candidate for drug development and nutraceutical formulation. Future research efforts should focus on elucidating its molecular mechanisms of action, optimizing its pharmacokinetic profile, and conducting clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety in humans. Harnessing the full therapeutic potential of luteolin could lead to the development of novel preventive and therapeutic strategies for combating oxidative stress-related diseases and improving human health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Luteolin
What is luteolin?
Luteolin is a naturally occurring flavonoid present in many fruits, vegetables, and herbs. It is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties.
What foods are high in luteolin?
Luteolin is found in high concentrations in foods such as parsley, celery, thyme, green peppers, chamomile tea, and citrus fruits.
What are the health benefits of luteolin?
Luteolin has been studied for its potential benefits in reducing inflammation, protecting against cancer, improving brain function, and supporting cardiovascular health. It also has antioxidant properties that help combat oxidative stress.
How does luteolin work as an anti-inflammatory?
Luteolin inhibits the activity of certain enzymes and signaling pathways involved in the inflammatory response, thereby reducing inflammation at the cellular level.
Can luteolin help with allergies?
Yes, luteolin has been shown to inhibit the release of histamines and other inflammatory mediators, which may help reduce allergic reactions.
Is luteolin effective for brain health?
Research suggests that luteolin may have neuroprotective effects, potentially aiding in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's by reducing brain inflammation and oxidative stress.
Are there any side effects associated with luteolin supplementation?
Luteolin is generally considered safe when consumed in dietary amounts. However, in high doses, it may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, or allergic reactions in some individuals.
How much luteolin should I take daily?
There is no established daily recommended dose for luteolin. However, typical doses used in supplements range from 50 mg to 100 mg per day. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Can luteolin be taken with other supplements or medications?
Luteolin may interact with certain medications, especially those that are metabolized by the liver. It's important to consult a healthcare provider before combining luteolin with other supplements or medications.
Is luteolin safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
There is limited research on the safety of luteolin during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is advisable to avoid luteolin supplements during these periods unless recommended by a healthcare provider.
Does luteolin have any anti-cancer properties?
Some studies suggest that luteolin may inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in certain types of cancer. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness as a cancer treatment.
Where can I buy luteolin supplements?
Luteolin supplements can be found in health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers. It’s important to choose a reputable brand to ensure quality and safety.
Can luteolin improve skin health?
Luteolin's antioxidant properties may help protect the skin from damage caused by UV rays and other environmental factors, potentially reducing signs of aging and improving overall skin health.
How should luteolin supplements be stored?
Luteolin supplements should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to maintain their potency.
Is luteolin suitable for vegans and vegetarians?
Yes, luteolin is a plant-derived compound and is suitable for both vegans and vegetarians.
These FAQs provide a broad overview of luteolin and its potential benefits, along with considerations for use and safety.
Explore the Perfect Health Sciences Website

The information on this site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment immediately. Our products are intended to be refrigerated.
Email us at support@perfecthealthsciences.com. Our mailing address is #113-14088 Riverport Way, Richmond, BC, V6W 0A7.