
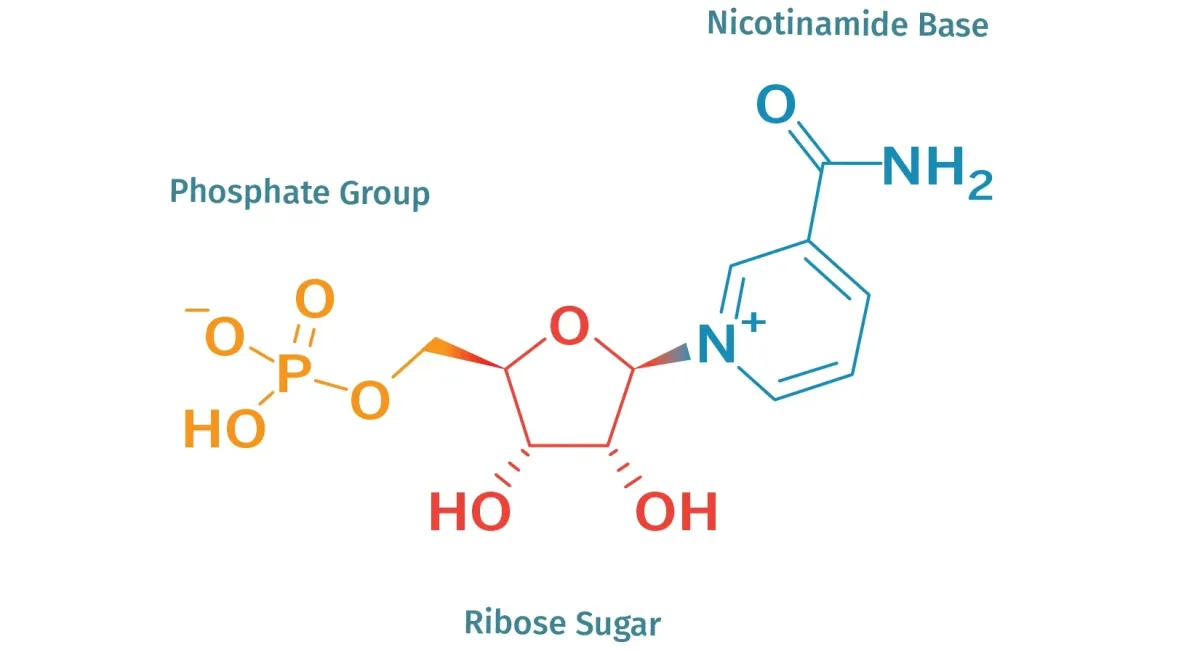
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
Abstract:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising molecule with diverse biological functions and therapeutic implications. This comprehensive review provides an in-depth analysis of NMN, covering its role as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), mechanisms of action, and potential applications in health and disease. Key findings from preclinical and clinical studies are synthesized, highlighting NMN's impact on cellular metabolism, energy production, DNA repair, and longevity. Furthermore, safety considerations, dosage regimens, and future research directions are discussed to elucidate NMN's therapeutic potential and optimize its clinical translation.
Keywords: Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, NMN, NAD+, Biological Significance, Mechanisms of Action, Therapeutic Potential, Preclinical Studies, Clinical Trials.
1. Introduction:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is an essential precursor in the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme involved in numerous cellular processes, including metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. In recent years, NMN has garnered significant attention for its potential health benefits and therapeutic applications. This review provides a comprehensive overview of NMN, elucidating its biological significance, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic potential in various disease conditions.
What is NMN?
NMN, or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is a molecule that occurs naturally in all forms of life. It's a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a coenzyme found in every cell of the body, which plays a crucial role in energy production, DNA repair, and overall cellular function. As we age, levels of NAD+ in our cells decline, leading to a decrease in cellular efficiency and vitality. Supplementing with NMN can help boost NAD+ levels, potentially slowing down or even reversing aspects of the aging process.
The Science Behind NMN
Research into NMN has revealed its significant potential in promoting health and longevity. Studies conducted on animals have shown that NMN supplementation can improve metabolism, enhance physical endurance, and even extend lifespan. While human studies are still in their early stages, preliminary results are promising, suggesting similar benefits in enhancing energy levels, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
Benefits of NMN
• Enhanced Cellular Energy: NMN boosts NAD+ levels, which are vital for the mitochondria—the powerhouses of our cells—to produce energy efficiently.
• DNA Repair and Cellular Health: NAD+ is essential for activating enzymes that repair damaged DNA, helping to maintain cellular integrity and function.
• Metabolic Improvement: NMN has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and support healthy metabolic functions, which can be beneficial for weight management and metabolic disorders.
• Cognitive Function: Higher NAD+ levels may enhance brain function, improving memory, focus, and overall cognitive health.
• Longevity and Anti-Aging: By supporting cellular repair and maintenance, NMN may contribute to a slower aging process and improved lifespan.
How to Take NMN
NMN is typically available in powder or capsule form. For beginners, it's advisable to start with a lower dose, such as 250 mg per day, and gradually increase as needed. It's best taken in the morning to coincide with the body's natural circadian rhythm and NAD+ production. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it's appropriate for your individual health needs.
Potential Side Effects
While NMN is generally considered safe, some users may experience mild side effects such as digestive discomfort or nausea. These are usually temporary and can often be alleviated by adjusting the dosage or taking NMN with food.
The Future of NMN
The field of NMN research is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries continually emerging. As scientists gain a deeper understanding of how NMN and NAD+ influence health and aging, the potential applications of NMN could expand, offering even greater benefits for maintaining vitality and longevity.
NMN represents a promising frontier in the quest for enhanced health and longevity. By understanding its role in cellular function and the potential benefits it offers, you can make an informed decision about whether NMN is right for you. Remember, while NMN supplementation can support health, it's most effective when combined with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle. Welcome to a new chapter in your wellness journey with NMN!
2. Biological Significance of NMN:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) plays a pivotal role in cellular metabolism as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a key cofactor involved in redox reactions and energy metabolism. By replenishing NAD+ levels, NMN contributes to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and optimal physiological function. Furthermore, NMN is involved in DNA repair mechanisms, contributing to genomic stability and cellular integrity.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a crucial molecule involved in cellular metabolism and energy production. Its significance in biological systems can be attributed to its role as a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential coenzyme in various cellular processes.
Key Points:
• Role in NAD+ Biosynthesis: NMN is a direct precursor to NAD+, which is vital for the function of sirtuins, enzymes involved in aging and longevity. NAD+ is necessary for energy production in cells, particularly in the mitochondria, where it facilitates oxidative phosphorylation.
• Metabolic Health: NMN supplementation has been shown to improve metabolic functions. It enhances insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, which can be beneficial for managing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
• Anti-Aging Properties: NMN helps maintain cellular energy levels, which decline with age. By boosting NAD+ levels, NMN supports DNA repair, reducing the accumulation of damage that contributes to aging.
• Cardiovascular Health: NMN has potential benefits for heart health by improving the function of endothelial cells, which line blood vessels. It may help prevent age-related vascular dysfunction and promote healthy blood flow.
• Neuroprotection: NMN's ability to raise NAD+ levels can support brain health. It may protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's by enhancing neuronal survival and function.
• Muscle Function and Endurance: NMN has been linked to improved muscle function and physical endurance. It enhances mitochondrial function in muscle cells, potentially improving exercise performance and reducing fatigue.
• Immune Function: NAD+ plays a role in the immune response, and NMN supplementation can help maintain immune system efficiency. It may assist in the prevention of age-related decline in immune function.
• Liver Health: NMN supports liver function by improving fat metabolism and reducing inflammation. It may protect against liver diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
• Research and Evidence: Research into NMN and its biological significance is ongoing, with numerous studies conducted on animal models showing promising results. Human clinical trials are also underway, aiming to validate the benefits observed in preclinical studies.
3. Mechanisms of Action of NMN:
• 3.1. NAD+ Biosynthesis: NMN serves as a substrate for the enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT), which catalyzes the conversion of NMN to NAD+. This enzymatic reaction is essential for maintaining adequate NAD+ levels and supporting cellular energy production.
• 3.2. Mitochondrial Function: NMN supplementation has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and biogenesis, leading to increased ATP production and improved cellular energy metabolism. By optimizing mitochondrial activity, NMN may mitigate age-related decline and enhance overall health and vitality.
• 3.3. DNA Repair and Genomic Stability: NMN participates in DNA repair pathways, such as the base excision repair (BER) pathway, by providing the necessary substrate for DNA polymerases and DNA ligases. This contributes to the maintenance of genomic integrity and protects against DNA damage-induced cellular dysfunction and senescence.
Conversion to NAD+
• NMN enters cells and is quickly converted into NAD+.
• NAD+ is essential for several critical biological processes.
Energy Production
• NAD+ is a key player in cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy.
• In cellular respiration, glucose and fatty acids are converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
• NAD+ helps in transferring electrons during this process, making it possible to produce ATP efficiently.
DNA Repair
• NAD+ is involved in DNA repair mechanisms.
• It activates enzymes called PARPs (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases), which detect and repair damaged DNA.
• This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of our genetic information.
Gene Expression
• NAD+ influences gene expression by activating proteins called sirtuins.
• Sirtuins help regulate various biological processes, including aging, inflammation, and stress resistance.
• When NAD+ levels are high, sirtuins can work more effectively.
Metabolic Function
• NAD+ is important for metabolic pathways that convert food into energy.
• It supports processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation.
Cell Signaling
• NAD+ acts as a signaling molecule, influencing cellular communication.
• It helps cells respond to changes in their environment and maintain homeostasis (balance).
Aging and Longevity
• As we age, NAD+ levels decline, leading to reduced efficiency in these vital processes.
• Increasing NMN intake can help boost NAD+ levels, potentially improving energy metabolism, enhancing DNA repair, and promoting healthy aging.
How Do We Get NMN?
• Dietary Sources: NMN is found in small amounts in foods like broccoli, cabbage, cucumber, avocado, and edamame.
• Supplements: NMN supplements are available and can help increase NAD+ levels more directly.
Potential Benefits of NMN Supplementation
• Increased Energy: By boosting NAD+ levels, NMN may help improve overall energy levels.
• Enhanced Physical Performance: Higher NAD+ levels can improve muscle function and endurance.
• Cognitive Function: NMN might support brain health by improving mitochondrial function and protecting neurons.
• Healthy Aging: NMN supplementation could promote longevity and reduce age-related decline.
Summary
NMN is a precursor to NAD+, a crucial molecule for energy production, DNA repair, and overall cellular function.
Supplementing with NMN can help maintain NAD+ levels, supporting various bodily functions and potentially promoting healthier aging.
By understanding these basic mechanisms, you can appreciate how NMN plays a significant role in maintaining our health and vitality.
4. Therapeutic Potential of NMN:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) holds significant therapeutic potential in various disease conditions, owing to its role in cellular metabolism, DNA repair, and mitochondrial function. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NMN supplementation in ameliorating age-related decline, metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular conditions. Furthermore, clinical trials exploring the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans have shown promising results, with improvements observed in metabolic parameters, cognitive function, and overall health outcomes.
The therapeutic potential of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a topic of considerable interest in scientific and medical communities. Here’s a simplified breakdown of its potential benefits:
Anti-Aging Effects
• NAD+ Boost: NMN increases levels of NAD+, which decline with age. Higher NAD+ levels can help maintain cellular functions and promote longevity.
• Sirtuin Activation: Sirtuins, proteins influenced by NAD+, play a role in aging and metabolic regulation. Boosting NAD+ through NMN can enhance sirtuin activity, potentially slowing down aging processes.
Energy Metabolism
• Mitochondrial Function: NAD+ is essential for mitochondrial function, the powerhouse of cells. Improved mitochondrial function can lead to better energy production and reduced fatigue.
• Muscle Performance: Enhanced energy metabolism can improve muscle strength and endurance, beneficial for both athletic performance and daily activities.
Neuroprotection
• Brain Health: NMN may support brain function by enhancing mitochondrial health and reducing oxidative stress. This can protect neurons from damage, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
• Cognitive Function: Improved NAD+ levels can support better cognitive function, including memory and learning.
Metabolic Health
• Insulin Sensitivity: NMN has shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and preventing type 2 diabetes.
• Fat Metabolism: Enhanced NAD+ levels can improve fat metabolism, helping in weight management and reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions.
Cardiovascular Health
• Blood Vessel Function: NMN can improve the function of endothelial cells lining the blood vessels, promoting better blood flow and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
• Heart Function: By enhancing energy metabolism, NMN can support heart muscle function, potentially reducing the risk of heart failure.
DNA Repair
• Genomic Stability: NAD+ is crucial for activating enzymes involved in DNA repair, such as PARPs. Better DNA repair mechanisms can reduce mutations and the risk of cancer.
• Cellular Health: Improved DNA repair helps maintain cellular health, reducing the incidence of age-related diseases.
Immune Function
• Immune Response: NMN may enhance immune cell function, helping the body better respond to infections and reducing the impact of age-related immune decline.
• Inflammation Reduction: By modulating immune responses, NMN can help reduce chronic inflammation, a key factor in many age-related diseases.
Potential Applications in Specific Diseases
• Diabetes: By improving insulin sensitivity and pancreatic function, NMN shows promise in managing and potentially reversing type 2 diabetes.
• Neurodegenerative Diseases: NMN's neuroprotective effects could be beneficial in conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis).
• Cardiovascular Diseases: Enhanced NAD+ levels can improve heart and blood vessel health, reducing the risk of conditions like hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure.
Enhancing Physical Performance
• Athletic Performance: Increased energy production and improved muscle function can enhance athletic performance and recovery.
• Muscle Recovery: NMN can support faster recovery from exercise by improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress.
5. Safety Considerations and Dosage Regimens:
• 5.1. Safety Profile: NMN is generally well-tolerated in both preclinical and clinical studies, with few reported adverse effects. However, long-term safety data are limited, and further research is needed to assess the potential risks associated with prolonged NMN supplementation.
• 5.2. Dosage Regimens: Optimal dosage regimens for NMN supplementation remain to be elucidated, with dosages ranging from 100 mg to 1000 mg daily used in clinical studies. Individual factors such as age, health status, and metabolic rate may influence the optimal dosage of NMN required to achieve therapeutic effects.
6. Future Directions and Research Opportunities:
• 6.1. Elucidating Mechanistic Pathways: Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying NMN's therapeutic effects, including its impact on cellular signaling pathways, gene expression regulation, and epigenetic modifications.
• 6.2. Clinical Translation: Continued clinical trials are warranted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in diverse patient populations and disease conditions. Long-term longitudinal studies are needed to assess the sustained benefits of NMN on health outcomes and longevity.
• 6.3. Combination Therapies: Investigating the synergistic effects of NMN with other therapeutic interventions, such as calorie restriction, exercise, and pharmacological agents, may offer novel treatment strategies for age-related diseases and promote healthy aging.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) represents a promising molecule with diverse biological functions and therapeutic implications. By serving as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NMN plays a critical role in cellular metabolism, DNA repair, and mitochondrial function. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the potential of NMN supplementation in ameliorating age-related decline and improving health outcomes in various disease conditions. However, further research is needed to elucidate its mechanisms of action, optimize dosage regimens, and assess long-term safety and efficacy. With continued investigation, NMN holds the promise of revolutionizing therapeutic approaches to aging-related diseases and promoting healthy longevity.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a popular topic of interest within the realm of longevity research and anti-aging interventions. Its association with the NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) pathway, a crucial coenzyme involved in cellular metabolism and energy production, has sparked enthusiasm among scientists and health enthusiasts alike. Several prominent proponents of NMN have contributed to the understanding of its potential benefits, drawing from a wealth of scientific literature to support its role in promoting healthspan and extending lifespan.

Dr. David Sinclair:
Dr. David Sinclair, a renowned geneticist and professor at Harvard Medical School, stands out as one of the most vocal proponents of NMN supplementation. His groundbreaking research on aging and longevity has shed light on the importance of NAD+ in cellular function and the potential of NMN as a precursor to NAD+ synthesis. Sinclair's studies, including seminal papers published in prestigious scientific journals such as Nature and Science, have demonstrated the efficacy of NMN supplementation in reversing age-related decline and extending lifespan in animal models.
Dr. Shin-ichiro Imai:
Dr. Shin-ichiro Imai, a professor at Washington University School of Medicine, has made significant contributions to the field of aging research, particularly regarding the role of NAD+ metabolism in health and longevity. His work has elucidated the mechanisms by which NMN supplementation can enhance NAD+ levels and activate sirtuins, a class of proteins involved in cellular regulation and stress response. Through rigorous experimentation and meticulous analysis, Imai has provided compelling evidence supporting the efficacy of NMN in promoting metabolic health and delaying aging-related pathologies.
Dr. Leonard Guarente:
Dr. Leonard Guarente, a professor at MIT and co-founder of Elysium Health, has been instrumental in translating scientific discoveries into practical interventions for aging-related conditions. Guarente's research on the sirtuin pathway and its modulation by NAD+ precursors, including NMN, has laid the foundation for the development of anti-aging supplements targeting cellular rejuvenation. His advocacy for NMN supplementation as a means to support NAD+ levels and mitigate age-associated decline has catalyzed interest in the field and fueled ongoing clinical investigations.
Dr. Junichi Sadoshima:
Dr. Junichi Sadoshima, a professor at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, has conducted pioneering research on the cardiovascular benefits of NMN supplementation. His studies have demonstrated the protective effects of NMN against age-related cardiovascular dysfunction, including hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy, and endothelial dysfunction. Sadoshima's work underscores the potential of NMN as a preventive and therapeutic agent for cardiovascular diseases, offering new avenues for intervention in age-related pathologies beyond metabolic health
Dr. Vadim N. Gladyshev:
Dr. Vadim N. Gladyshev, a professor at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women's Hospital, has investigated the role of NAD+ metabolism in aging and age-related diseases from a systems biology perspective. His interdisciplinary approach combines computational modeling, experimental validation, and clinical translation to unravel the complexities of NMN-mediated pathways and their impact on organismal health. Gladyshev's integrative studies provide valuable insights into the multifaceted effects of NMN supplementation on cellular homeostasis and organismal resilience to stressors.
In summary, the proponents of NMN, including Dr. David Sinclair, Dr. Shin-ichiro Imai, Dr. Leonard Guarente, Dr. Junichi Sadoshima, and Dr. Vadim N. Gladyshev, have collectively advanced our understanding of NMN's potential as a therapeutic agent for promoting healthspan and longevity. Their contributions, rooted in rigorous scientific inquiry and empirical evidence, have catalyzed ongoing research efforts aimed at harnessing the benefits of NMN supplementation for mitigating age-related decline and enhancing overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is NMN?
Answer: NMN stands for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, a molecule derived from vitamin B3 (niacin) that serves as a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), which is essential for energy production and various cellular processes.
2. What are the benefits of NMN?
Answer: NMN supplementation is believed to boost NAD+ levels, which can enhance energy metabolism, improve mitochondrial function, support DNA repair, promote healthy aging, enhance cognitive function, and improve cardiovascular and metabolic health.
3. How does NMN work in the body?
Answer: Once ingested, NMN is converted into NAD+ within cells. NAD+ plays a critical role in cellular respiration, DNA repair, gene expression regulation via sirtuins, and overall energy production.
4. Is NMN safe to use?
Answer: Early studies and small-scale clinical trials suggest that NMN is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, more extensive and long-term studies are needed to confirm its safety profile.
5. What is the recommended dosage of NMN?
Answer: There is no universally established dosage for NMN supplementation. Studies have used varying dosages, typically ranging from 250 mg to 500 mg per day. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting NMN supplementation.
6. Can NMN help with aging and longevity?
Answer: Research suggests that NMN may help counteract age-related declines in NAD+ levels, potentially improving energy metabolism, supporting DNA repair, and enhancing overall cellular function, which could contribute to healthier aging and increased longevity.
7. What foods are high in NMN?
Answer: NMN is found in small amounts in foods like broccoli, cabbage, cucumber, avocado, edamame, and tomatoes. However, the quantities in food are typically much lower than those used in supplements.
8. How does NMN compare to NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)?
Answer: Both NMN and NR are NAD+ precursors and are believed to increase NAD+ levels in the body. NMN is a direct precursor to NAD+, while NR is first converted into NMN before becoming NAD+. Both have shown promise in research, but NMN is often considered to be more directly involved in the NAD+ biosynthesis pathway.
9. Are there any side effects of taking NMN?
Answer: Most studies report minimal side effects. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms like nausea, headache, or digestive discomfort. Long-term safety and potential side effects are still under investigation.
10. Can NMN improve cognitive function?
Answer: NMN may support cognitive function by enhancing mitochondrial health and reducing oxidative stress in the brain. This could potentially protect neurons and improve memory and learning abilities, particularly in aging populations.
11. Is NMN suitable for everyone?
Answer: While NMN shows potential benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen.
12. How long does it take to see the effects of NMN?
Answer: The time frame for experiencing the benefits of NMN can vary. Some people may notice improvements in energy levels and cognitive function within a few weeks, while others may require several months of consistent use to observe significant changes.
13. What are the potential therapeutic applications of NMN?
Answer: Potential therapeutic applications of NMN include treatment for age-related diseases, metabolic disorders like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, and improving overall physical and cognitive performance.
14. Can NMN be taken with other supplements or medications?
Answer: NMN can often be taken with other supplements, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure there are no adverse interactions with medications or other supplements you may be taking.
15. Where can I buy NMN supplements?
Answer: NMN supplements are available from various health stores, pharmacies, and online retailers. It is important to choose reputable brands that offer high-quality, pure NMN products to ensure safety and efficacy.
These FAQs should provide a comprehensive overview for anyone curious about NMN and its potential benefits.
Explore the Perfect Health Sciences Website

The information on this site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment immediately. Our products are intended to be refrigerated.
Email us at [email protected]. Our mailing address is #113-14088 Riverport Way, Richmond, BC, V6W 0A7.